Welcome To Week 16
Your Baby: The First Flutters
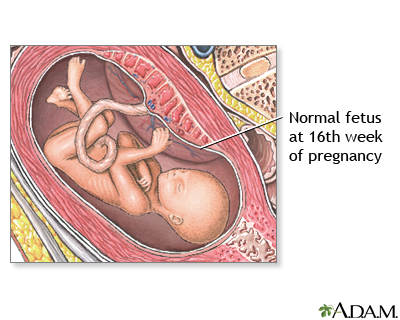
The fetus measures 4.3-4.6 inches (12 cm) from crown to rump and weighs about 2.8 ounces (80 g). Despite its growing body, your fetus has plenty of room to move around within the uterus. Its head is erect, its legs are now longer than its arms, and its limb movements are becoming more coordinated. Its fingers and toenails are constantly growing and are now well formed. If you're eager to find out the gender and you're due for an ultrasound, you may be in luck -- as long as the baby cooperates.
Your Body: All About Amnios
- What is it? An amniocentesis, more often referred to as amnio, is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through a woman's abdomen into the uterus to remove a small amount of amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus. An ultrasound is used to guide the needle into an area of the uterus away from the fetus. Since the fluid and the fetus are formed from the same cells and have the same genetic makeup, the fluid undergoes genetic analysis and biochemical tests in a lab.
- What is the purpose of the test? One of the most common uses of the amnio is to identify genetic or chromosome abnormalities in the baby such as Down syndrome. It can also detect other conditions, including: genetic disorders known to run in the family, neural tube defects such as anencephaly and spina bifida, Rh disease, and fetal lung assessment (the last two are done during the last half of the pregnancy).
- Who takes the test? Between 80% to 90% of all amnios are done when women are over 35 years of age or will turn 35 before their due date. It is also performed if the results of the quadruple screen test -- MSAFP, inhibin A, estriol, and/or hCG -- are abnormal. Other reason for an amnio include:
- if a couple has had a child with a chromosomal abnormality (i.e., Down syndrome) or with a metabolic disorder (i.e., Hunter's syndrome);
- if a couple has had a child or a close relative with a neural tube defect;
- when the mother is a carrier of an x-linked genetic disorder (i.e., hemophilia);
- when both parents are carriers of an autosomal recessive inherited disorder, such as Tay Sachs disease or sickle cell anemia;
- if one parent has a condition passed on by autosomal dominant inheritance (i.e., Huntington's chorea);
- if the woman has to deliver early and the baby's lungs have to be assessed.
- When is the test taken? If the amnio is taken for chromosome analysis or molecular DNA analysis, it is typically performed between 16 and 18 weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, however, the test may be done up to a month earlier. If it is to assess fetal lungs, it may be taken shortly before delivery.
- How safe is it? The risk of an amnio causing a miscarriage ranges from 1 in 200 to 1 in 400. When it does happen, it is usually because of an infection in the uterus, the water breaking, or labor being induced prematurely. While the numbers are small, the test should be done only when the benefits outweigh the risks.
You should talk to your health care provider about whether or not you should have an amnio performed based on your individual risk and indications.
On That Note: Amnio On View
For some women, amniocentesis is just another routine pregnancy procedure -- part and parcel of the nine-month odyssey. For others, it is an unnerving exam that makes them think twice. Either way, you can put your mind at ease with this visual presentation.
Weekly Tip
Many pregnant women get their best sleep during the second trimester. After all, your breasts are no longer tender, your tummy is finally stable, and some of the first-trimester aches and pains have dissipated. So before you really get heavy and uncomfortable in the next trimester, try and stock up on some extra sleep now. Lounge around in bed on the weekend, or crawl into bed early and read a few more pages than usual. Revel in repose. It might seem like an eternity before you have this opportunity again.
Review Date: 2/6/2007
Reviewed By: Douglas A. Levine, MD, Gynecology Service, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.
The information provided should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Adam makes no representation or warranty regarding the accuracy, reliability, completeness, currentness, or timeliness of the content, text or graphics. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.